Longbottom D, Coulter LJ. National Health and Medical Research varying severity with possible extrapulmonary can occur. Clinical Features Clinical presentations of. Symptoms include a severe skin eruption, fever, hematological abnormalities eosinophilia or atypical lymphocytosis and internal organ involvement.
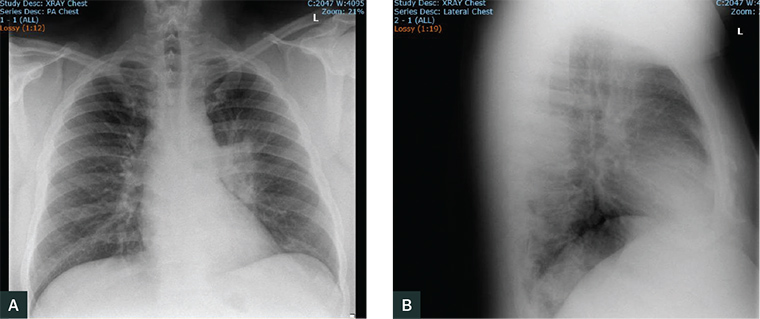
Chlamydia psittaci is a gram-negative, obligate intracellular organism. Birds are the main reservoir, but also non-avian domestic animals and humans can be infected. In humans it mostly causes respiratory infections due to occupational exposure with varying severity. Sensitive and specific diagnostic tests are needed to define psittacosis in humans as these tests also allow rapid tracing of the animal source. However, diagnosis in humans is often based on time-consuming culture techniques and antibody detection assays as in many countries, the existing molecular diagnostic tests for psittacosis are not reimbursed by the public health insurance. Blood analysis showed signs of inflammation with mild eosinophilia. Chest CT showed multiple peripheral ground glass opacities with consolidation in both lungs.
NCBI Bookshelf. Justin Chu ; Muhammad I. Authors Justin Chu 1 ; Muhammad I. Durrani 2. Psittacosis represents a zoonotic bacterial infectious disease caused by the obligate intracellular organism, Chlamydia psittaci. Psittacosis, which is also called parrot fever and ornithosis, is transmitted from contact with infected birds and causes a wide-ranging spectrum of disease and severity. Birds serve as the major epidemiological reservoir and while birds from the order Psittaciformes parakeets, parrots, lories, cockatoos, and budgerigars and Galliformes chickens, turkeys, pheasants are commonly identified, this disease process can occur in any bird species and has been documented in species from 30 different orders of birds.
